Salmonella Typhi symptomsNature of pathogenicity of typhoid
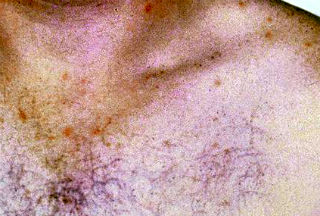
10 ^ 5 cells must be ingested to cause typhoid fever. After incubation for 7-24 hours to three days maximum, the first symptoms appear mild fever to rise gradually up to 39-40 ° C accompanied by increasing fatigue, abdominal distension, constipation, abdominal pain, frontal headaches , colic, fatigue, dizziness, insomnia, oliguria, apathy, rash, malaise, anorexia, nausea and vomiting. Diarrhea usually occurs during the period of state, and the stools are liquid, fetid, yellowish frequent but not constant (60 to 70%) and may be bloody. The fever is constant, so-called plateau between 39-40 ° C, sometimes with chills and dissociation pulse. There are severe abdominal pain and continuous (20 to 40%) and anorexia ie a tuphos of prostration, delirium and indifference moderate (30-45%). Physical examination can detect at this stage a typical sensitivity of the right iliac fossa (called gurgling), moderate splenomegaly and, less frequently, rose spots on the abdomen, flanks and base of the thorax, ulcers ( of Duguet) surface of the anterior pillars of the soft palate, finally rhonchi. The pathogen can be found in the stool. The evolution of this disease is usually not serious and prompt treatment can last several weeks resulting in death. It is primarily a lymphatic origin of sepsis. After reaching the gastrointestinal tract, Salmonella typhi rapidly invades the intestinal mucosa, it may even multiply within the phagocytes and the lamina propria, it lead to their death and escape later. Moreover, this bacterium colonizes the mesenteric lymph nodes, from there they spread into the lymph chest and into the systemic circulation. On the other hand, lysis of bacteria in the lymph releases the toxic LPS or endotoxin lipopolysaccharide O (related to the Ag O). It is a complex carbohydrate and lipid-polypeptide. Endotoxin O is spoofed in the blood, causes local ulceration (perforation) of Peyer's patches (hemorrhagic intestinal lesions) by irritation of the abdominal sympathetic, conveyed to the cerebral ventricles determines the tuphos this state of stupor, prostration, nervous disorders or depression, diarrhea with abdominal pain and is also the endotoxin which, acting on the thermoregulatory center, causes fever to 40 ° C. This endotoxin is heat (heat resistant 100 ° C and alcoolostable and destroyed by formalin 0.5%. This bacterium is a facultative intracellular parasite sample. The clinical symptoms become evident when the bacteria then invade the blood. Then, the bile ducts are infected, the multiplication of bacteria in bile releases millions of bacteria in the intestines, where the presence of the pathogen in the stool. S. typhi can also spread to other tissues or organs with blood. Gallbladder, bone marrow and spleen may be possible sources of infection. This explains relapse. Treatment consists of antibiotic therapy with molecules that will ensure good concentration node. It is recommended that chloramphenicol, bactrim (in the case of antibiotic resistance) and thiamphenicol for treatment. Ampicillin is also used which can also treat chronic carriers. Colimycin is interesting in severe gastroenteritis. Chloramphenicol is bacteriostatic only, and is toxic, but we know he goes through the nodes, haunts of bacilli. In cases of typhoid fever, do not use too strong emblem doses of this antibiotic. The destruction of a large number of Salmonella would release large amounts of glucose and lipid-toxin polypeptide, strongly irritating the neuro-vegetative and triggering a fatal malignant syndrome. Prevention of typhoid feverVaccine (TABC), detection of healthy carriers, they host the state commensal organism in the gallbladder without showing disorders, and may shed up to 10 ^ 11 organisms per gram of faeces. Biochemist Rene Germanier changed the genetic heritage of the bacterium, so it absorbs galactose in such quantities that it becomes unable to metabolize and that the mutant expires poisoned after having had time to develop in the intestinal immune response, but before he forced the body to produce toxins. |
|
© 2014 "salmonellatyphi.org". All Rights Reserved |